Architecture
Overview¶
KICS is 100% open source is written in Golang using Open Policy Agent (OPA).
Golang speed, simplicity and reliability made it the perfect choice for writing KICS, while Rego as a query language, was a native choice to implement security queries.
So far have written 1000+ ready-to-use queries that cover a wide range of vulnerabilities checks for AWS, GCP, Azure and other cloud providers.
High Level Architecture¶
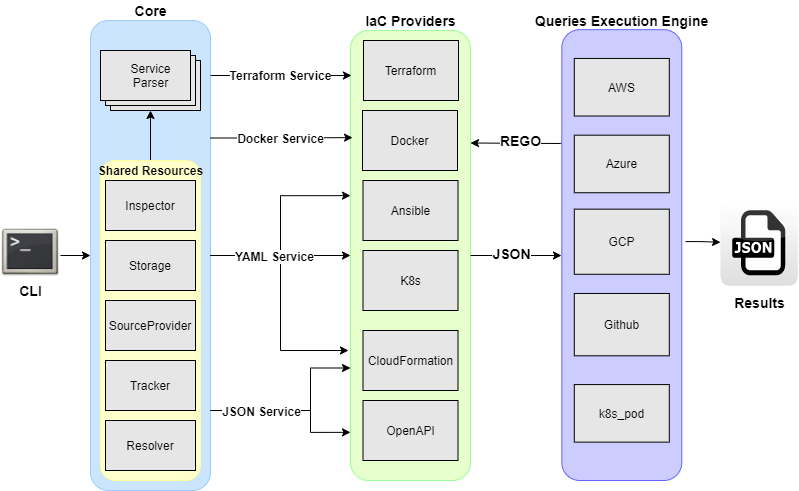
KICS has a pluggable architecture with extensible pipeline of parsing IaC languages, which allows an easy integration of new IaC languages and queries.
At a very high level, KICS is composed of the following main components: a command line interface, parser, queries execution engine, IaC providers, security queries, and results writer.
- Command Line Interface => Provides CLI input to KICS.
- Parser => responsible for parsing input IaC files (terraform and others)
- IaC Providers => Converts IaC language into normalized JSON
- Queries Execution Engine => applies REGO queries against normalized JSON
- Security Queries => pre-built REGO queries for each security and misconfiguration
- Writer => Writes results into JSON format
Execution Flow¶
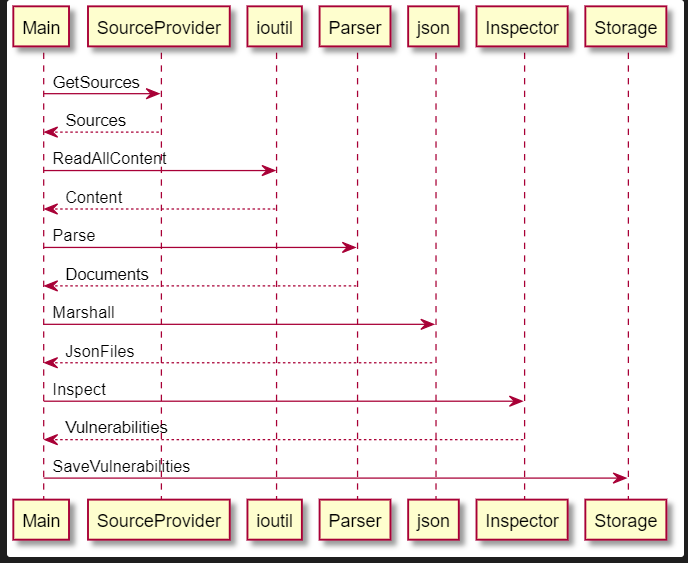
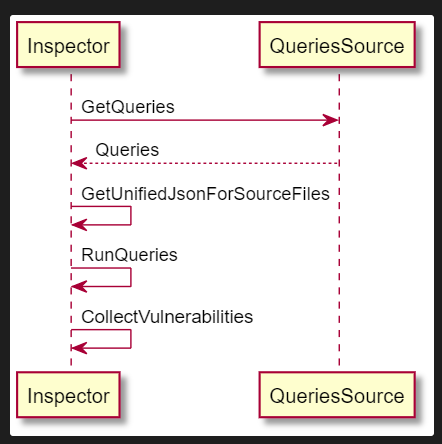
The sequence diagram below depicts interaction of the main KICS components:
Concurrent Scans¶
KICS creates multiple services, each containing a unique parser. All the services will then concurrently generate a payload and run queries on it according to its containing parser.
Concurrency exists on both the services representing each platform as well as the queries of each service. Each platform detected will run their queries concurrently with one another and the queries of each platform will themselves run concurrently using the number of workers passed on th.
When a vulnerability is found, it is saved inside the Storage which is shared amongst all the services.
- Paths => create services based on types of IaC files;
- Service => contains a unique parser and shares other resources with other services;
- Start Scan => Services will concurrently create payloads based on its parser, inspect for vulnerabilities and save them on the shared storage;
- Results => when all services have finished their execution all the results will be gathered from the storage.